Prolactin Levels
High Prolactin Levels
By Carolyn Coulam, M.D. and Nancy Hemenway
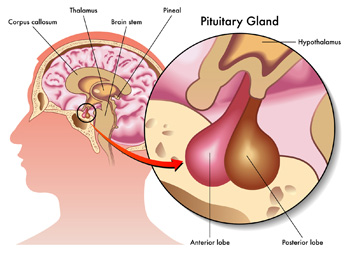
A basic work-up by a reproductive endocrinologist will likely include a variety of blood tests including prolactin levels. Prolactin is a hormone that is produced by the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland sits below the hypothalamus at the base of the brain.
What does Prolactin do?
Prolactin causes breasts to grow and develop. It also causes milk production in the breasts of a lactating or pregnant woman. Prolactin can be found in both males and females. A blood test will determine the prolactin levels and your doctor will have a normal or out of range level and recommend best course of action.
During pregnancy prolactin levels increase. After the birth of a baby, a woman’s estrogen and progesterone levels drop and prolactin levels rise. These high levels of prolactin cause milk to “come in” or milk production to begin so a baby can be breast fed. In women who are not pregnant, prolactin is one of the hormones that regulate menstrual cycles. In males high levels of prolactin may be related to sperm production and sexual dysfunction.
What is Hyperprolactinemia?
“Hyper” ( meaning over, super, or excess) or in this case Hyperprolactinemia – meaning one has an excess of prolactin or high prolactin levels. Hyperprolactinemia is a condition where non-pregnant women (or men) have too much or an excess of prolactin in their bodies. This condition is fairly common in women of reproductive age who are experiencing irregular periods but who have normal ovaries (about 30%). High prolactin levels may also interfere with estrogen and progesterone production. Prolactinemia can stop ovulation altogether.
Sometimes there are no symptoms and women will often discover they have high prolactin when they have trouble getting pregnant and go for fertility testing or because they need to regulate their irregular periods. Some women will start producing milk or a milky substance outside of a pregnancy (a condition called galactorrhea). In men with elevated levels prolactinemia can cause impotence or reduced libido (desire for sex). However, prolactinemia is more frequent in women than in men.
Common Causes
Prolactinemia causes vary. Some common causes include:
- Pituitary Tumors
- Under Active Thyroid (Hypothyroidism)
- Medications
- Antidepressants Medications
- Anti-psychotic Medication
- Anti-Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Medications
- Stress
- Excessive exercise
- Nipple Stimulation
- Some Foods (A recent research study appears to demonstrate one of the brain altering effects of gluten. In this case, a compound in gluten acts as an opioid chemical that leads to the excessive excretion of the neuro hormone, prolactin. More)
- Some Herbs may elevate prolactin levels (Fenugreek, Goat’s Rue, Red Raspberry Leaf and others)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – a scan of the brain checks for the presence of a tumor of the pituitary gland.
Treatment
Treatment is determined based on diagnosis. If there is evidence (MRI) of a pituitary tumor, for example, the usual treatment is medication. Hypothyroidism is treated by replacing the lack of hormone normally present with normal thyroid production. Follow ups with your doctor will determine if prolactin levels return to normal. If medication is found to be causing high prolactin levels, work with your doctor to find an alternative medication.
Medications used to treat elevated prolactin levels are cabergoline and bromocriptine. Treatment with these medications will usually continue until your symptoms lessen or pregnancy occurs.
These are category B classified medications.
Animal studies have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus; however, there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
or
Animal studies have shown an adverse effect, but adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women have failed to demonstrate a risk to the fetus.
Check with your doctor about how any medications should or should not be taken during pregnancy.
Cabergoline is taken once or twice a week and has been reported to have fewer side effects than bromocriptine. Cabergoline may drop prolactin levels back to normal range more quickly than bromocriptine.
Side Effects of Cabergoline (Trade Name – Dostinex) include:
Most Common Side Effects
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Constipation
- headache
Less serious side effects may include:
- Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, gas, indigestion, constipation;
- Headache, depressed mood;
- Dizziness, spinning sensation;
- Drowsiness, nervousness;
- Hot flashes;
- Numbness or tingly feeling; or.
- Dry mouth.
Bromocriptine can be prescribed in a suppository form to be inserted directly in the vagina. This is an off-label use of the medication.
Note: Not all women with elevated prolactin need treatment. Women with elevated levels of prolactin who don’t make estrogen will need treatment to increase estrogen production. If the cause is found to be a pituitary tumor, the woman may need no treatment if she is making estrogen. Birth control pills will help with regulation of periods.
An MRI baseline should be taken and the patients should be followed yearly with MRI for 3 years to record any changes in the small pituitary tumor.
Please check with your reproductive endocrinologist or physician for individual guidance on elevated prolactin.
